Disclaimer: This website provides health information for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have.
Cancer is a devastating disease affecting millions of people in the United States annually. It is a leading cause of death, and despite significant advances in research and treatment, there is still no cure.
Cancer happens when cells in the body grow out of control. There are many types of cancer, and they can start almost anywhere in the body. Some common types include breast cancer, colon cancer, and skin cancer. But nothing comes close to the devastating effects of lung cancer. Here’s what you need to know about this disease.
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are a pair of organs in the chest that help us breathe. They are made up of tiny air sacs called alveoli, connected by a network of small bronchioles tubes.
Cancerous cells can form in any part of the lung but most commonly in the cells lining the bronchioles. These cells can then grow and spread to other parts of the lung or other organs in the body.
There are two main types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer is much less common than non-small lung cancer but is more aggressive and harder to treat.
Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common type of lung cancer. This kind of cancer originates in the outer part of the lung and can then spread to the inner parts.
Lung cancer is challenging to treat because it is often diagnosed at a late stage when cancer has already spread to other body parts. Even with treatment, the survival rate is only about 18 percent.
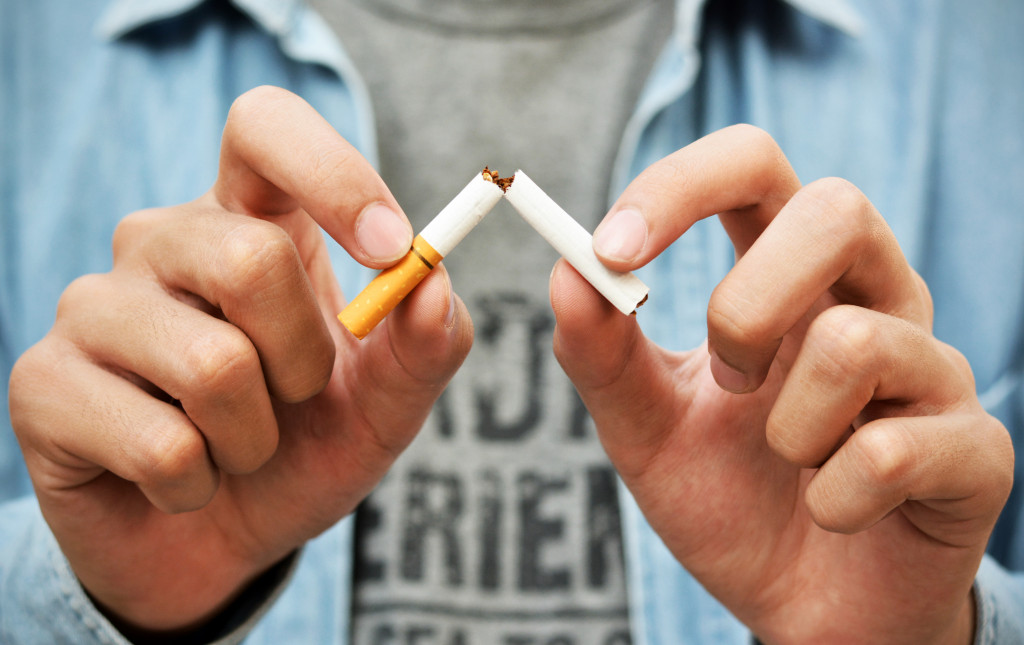

What Causes Lung Cancer?
The leading cause of lung cancer is smoking cigarettes. Cigarette smoke contains more than 7,000 chemicals, including 70 known to cause cancer. As a result, people who smoke are 15 to 30 times more likely to develop lung cancer than people who don’t smoke.
Secondhand smoke is also a significant cause of lung cancer. This is the smoke that comes from burning cigarettes, cigars, or pipes and the smoke exhaled by smokers. People exposed to secondhand smoke have a 20 to 30 percent higher risk of developing lung cancer.
Other risk factors for lung cancer include:
- Exposure to hazardous materials, such as asbestos or radon
- A family history of lung cancer
- Lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
All of these things contribute to lung cancer. Studies have also found that it can be hereditary, with 8% of lung cancer patients getting it from their parents.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer often doesn’t cause any symptoms in the early stages. This makes it difficult to diagnose and treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer has usually already spread to other body parts.
Common symptoms of lung cancer include:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Chronic cough
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss
- Coughing up blood
These are just some of the more common symptoms. If you are experiencing any of these, you must see a doctor as soon as possible for a diagnosis.
Dealing With Lung Cancer
There are many ways to deal with lung cancer, with some of the treatments prolonging the lives of some patients. The most common treatment is chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
This kind of treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be taken intravenously or in pill form. Chemotherapy is often combined with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy. Medical experts suggest that seniors get extra care when undergoing chemotherapy. Getting local palliative services can help boost the survival rates of seniors with lung cancer. Furthermore, it can improve their quality of life while going through chemotherapy.
Surgery
Surgery is usually only an option if the cancer is caught in the early stages. Then, the surgeon will remove the cancerous tissue and a margin of healthy tissue around it. There are different types of surgery for lung cancer, depending on how much of the lung needs to be removed.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses advanced technology, such as X-rays to kill cancer cells. Patients can use it alone or with other treatments, such as surgery or chemotherapy. Radiation therapy can be given externally, from a machine outside the body, or internally, from radioactive material placed directly into the tumor.
Targeted Drug Therapy
This is a newer type of treatment that specifically targets cancer cells without harming normal cells. Instead, these drugs work by interfering with the ability of cancer cells to grow and spread. Targeted drug therapy is often combined with other treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Lung cancer can be problematic once someone has developed it. However, a person can survive such an endeavor through proper treatment. Much like any other disease, preventing lung cancer is often better than getting treated for the disease.